The House of BRM
The House of BRM is a graphical representation intended to convey key aspects of a successful Business Relationship Management role, discipline, and organisational capability. The House of BRM illustrates three key aspects of Business Relationship Management as follows:The House of BRM explained

- The foundation supports the BRM role and ensures it has the Competencies to be effective and deliver value to both the Provider organisation and its Business Partners.
- The pillars define the BRM space in terms of BRM Core Disciplines—Demand Shaping, Exploring, Servicing, and Value Harvesting.
- The roof of the House of BRM protects Business Relationship Management as a key aspect of Provider capability. It does this by ensuring clarity around how the role, discipline and organisational capability of Business Relationship Management in the context of the Provider Strategy and Operating Model.
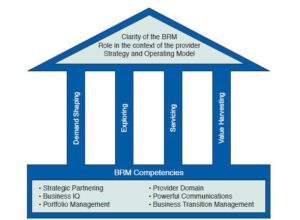
The Foundation
The foundation of the House of BRM outlines the competencies that a service provider would need to develop to ensure that Business Relationship Management can achieve its intended value. As the BRM builds the bridge between the Provider and the Business Partners, is is very important that he has the right knowledge, attitude and skills to function effectively. Most important, the BRM must be able to manage Business Transition both internally and with Business Partners. Business Transition Management ensures that business areas impacted by an initiative are identified, understand and are prepared for the business transition (not just the technology transition) so that disruption to business operations is minimised and the full value of the project is achieved.
The Pillars of the House of BRM
Business Relationship Management depends upon four Core Disciplines:
- Demand Shaping – The Demand Shaping Discipline stimulates, surfaces, and shapes business demand for Provider services, capabilities, and products. It ensures that business strategies fully leverage Provider capabilities, and that the Provider service portfolio and capabilities enable business strategies. Most importantly, Demand Shaping is focused on optimising the business value realised through Provider services, capabilities, and products—that low-value demand is suppressed while higher-value demand is stimulated.
- Exploring – The Exploring Discipline identifies and rationalises demand. Business Relationship Management helps sense business and technology trends to facilitate discovery and demand identification. Exploring is an iterative and ongoing process that facilitates the review of new business, industry, and technology insights with potential to create value for the business environment. The key benefit of this discipline is the identification of business value initiatives that will become part of the Provider portfolio of services, capabilities and products.
- Servicing – The Servicing Discipline coordinates resources, manages Business Partner expectations, and integrates activities in accordance with the Business Partner-Provider partnership. It ensures that Business Partner-Provider engagement translates demand into effective supply requirements. Servicing facilitates business strategy, Business Capability Roadmapping, portfolio and program management.
- Value Harvesting – The Value Harvesting Discipline ensures success of business change initiatives that result from the exploring and servicing engagements. Value Harvesting includes activities to track and review performance, identify ways to increase the business value from Business-Provider initiatives and services, and initiates feedback that triggers continuous improvement cycles. This process provides stakeholders with insights into the results of business change and initiatives.
The Roof in the House of BRM
Business Relationship Management is a component in the overall operating model of the Service Provider. A Provider Strategy describes the Provider Mission, Vision, Strategic Intents, Outcomes, Values, Principles, and Policies. A Provider Operating Model is an abstract representation of how an enterprise manages its Provider resources and assets in order to deliver against its Strategy, including Governance, Services, Processes, Organisation, and Metrics. The linkage between these Strategy and Operating Model components are important to the Provider’s ability to deliver business value. should be designed with the Provider Strategy in mind. The Operating Model must support the strategy.
While Provider organisations have traditionally been chartered with most of the primary responsibilities for management of a specific domain (e.g. Information Technology), the role of business executives, users and even end consumers is becoming important. Ultimately, value from Provider investments is realised within the business units and with external stakeholders. As such, Provider Operating Model must address the enterprise and its ecosystem of vendors, partners, and customers—not just the responsibilities of those within the Provider organisation.
Are you effectively performing the Business Relationship Management Role?
